Rosemary Oil for Hair Growth: Does it Work?

Rosemary Oil for Hair Growth: Does it Work? Rosemary oil is a popular choice for those looking to support hair growth. This essential oil has been used for centuries in various traditional medicines and is known for its stimulating, soothing, and healing properties. Recent research suggests that rosemary oil may also help improve the thickness of hair, reduce hair loss, and even promote new growth! What is Rosemary Essential Oil? Rosemary essential oil is derived from the fragrant leaves of the rosemary plant, which is native to the Mediterranean region. It has a woody and slightly sweet scent that’s often used in aromatherapy for its calming properties. The pine-needle shaped leaves of the rosemary plant are dried and then crushed so that the essential oil can be extracted. This is usually done by distillation, which involves boiling the plant matter and then condensing the steam to collect the oil. Rosemary essential oil contains a variety of compounds, including camphor, eucalyptol, and cineole. These substances are used individually as the active ingredient in a variety of common cosmetic dermatology products and may play a role in the hair stimulating effects of rosemary essential oil. Rosemary Essential Oil for Hair Loss In the past decade there has been a growing interest in the potential of rosemary essential oil for promoting hair growth and preventing baldness or alopecia. While research is still ongoing, there are several theories as to why this might be true. Some researchers believe that is that rosemary essential oil contains compounds that act as antioxidants, which may help protect the scalp from inflammation caused by free radicals. Additionally, some suggest that when applied topically, rosemary oil may increase circulation throughout the scalp, allowing more nutrients to reach the hair follicles, which stimulates hair growth. Some research also indicates that rosemary essential oil also has antimicrobial properties, meaning it could potentially reduce infection-related hair loss such as dandruff or fungus. Minoxidil vs. Rosemary Oil for Hair Growth Topical minoxidil is an FDA-approved medication for treating androgenetic alopecia in men and women. Minoxidil is the active ingredient in the popular over-the-counter hair loss product, Rogaine. Products like Rogaine are applied directly to the scalp in order to prevent hair loss and promote hair growth. These types of products are available as a liquid, foam, or gel and are typically one of the first medications suggested to those experiencing hair loss or thinning hair. In a 2015 study published in the peer-reviewed journal SKINmed, researchers sought to determine how topical 2% minoxidil compared to rosemary essential oils in treating patients with androgenetic alopecia. In this study, 50 patients received daily topical minoxidil treatments, while the other 50 received topical rosemary essential oils. The study examined the total hair count and the frequency of itchy scalp symptoms among patients over 6 months. Incredibly, the researchers found that the patients who received treatments of rosemary oil for hair growth had statistically similar outcomes to the patients who received minoxidil – and both groups saw improvements in hair growth! This suggest that for these patients, using rosemary oil for hair growth was just as effective as topical minoxidil – which is widely considered the gold standard topical medication to promote hair growth and reduce hair loss. Another fascinating finding of this study was that the group of patients who were treated with daily rosemary essential oils has less skin irritation and less incidences of itchy scalp that the minoxidil group. This is significant because skin irritation is one of the common side effects of topical minoxidil. This research suggests that rosemary essential oils may be an effective way to encourage hair growth in patients with sensitive skin who want to avoid skin irritation associated with minoxidil. Anti Inflammatory Properties of Rosemary Oil Rosemary oil is also used as an anti-inflammatory treatment, which may be beneficial for those suffering from scalp conditions such as psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis. These skin conditions can cause inflammation and redness on the scalp and contribute to hair loss. In particular, eucalyptol – one of the main compounds found in rosemary essential oil – is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have shown that eucalyptol has been effective in reducing inflammation caused by various skin diseases. This suggests that rosemary oil may potentially serve as a natural remedy for inflammatory scalp disorders such as psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis, which may improve hair growth outcomes for patients dealing with these conditions. Rosemary Oil Effects on Hair Follicles Studies on animal models have also suggested that rosemary essential oil may be able to stimulate hair follicles. One study in particular looked at the effects of rosemary essential oils on mouse hair follicles. In this study, researchers applied topical testosterone to the shaved backs of mice in order to attempt to prevent hair growth due to the androgenic affects of this sex hormone. One group of the mice also received topical rosemary oil treatments to see if it could counteract the affects of the testosterone an stimulate hair growth. The researchers found that the rosemary oil did, in fact, significantly block the testosterone from negatively impacting healthy hair growth. The researchers conclude that the rosemary oil could be a promising topical treatment for male and female pattern hair loss. Rosemary Oil Inhibits DHT Rosemary oil may also be beneficial to those suffering from genetic hair loss due to its ability to inhibit the production of a hormone known as dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is one of the primary causes of androgenetic alopecia, or male/female pattern baldness. In the rosemary mouse hair study, researchers determined that topical applications of rosemary oil effectively reduce concentrations of DHT. Although this study was performed on mice, the researchers believe that this finding is relevant to treating hair loss in humans. DHT blocking products are commonly prescribed or sold over-the-counter as a first defense for protecting scalp health and as a way to stimulate hair growth in those suffering from androgenic
Pumpkin Seed Oil for Hair Growth

Pumpkin Seed Oil for Hair Growth There’s a lot of buzz recently about using pumpkin seed oil to promote hair growth. As with any new health trend, it’s important to understand the facts before you jump on board and start using pumpkin seed oil as part of your hair care routine. In this article, we will discuss the science behind pumpkin seed oil for hair growth to help you understand if pumpkin seeds really contain the secret to healthier hair. History of Pumpkin Seed Oil for Hair Pumpkin seeds and pumpkin seed oil have long been used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat various conditions. In more recent years, pumpkin seed oil has become increasingly popular as an ingredient in commercial cosmetic products. Studies have shown that the oil contains several fatty acids and antioxidants which may help reduce inflammation, improve scalp circulation and promote hair growth. However, up until very recently there has been limited research conducted into how effective pumpkin seed oil is for promoting hair growth when applied topically or ingested orally. Can Pumpkin Seed Oil Promote Hair Growth? Recent research suggests that pumpkin seed oil may indeed help promote hair growth. Recently, a number of peer-reviewed studies have been published that seem to indicate that pumpkin seed oil may be an effective tool to treat hair loss and increase hair thickness. There are various approaches to treating hair loss with pumpkin seed oil. Some people taking pumpkin seed oil supplements to benefit from the nutritional value of pumpkin seeds. Others apply pumpkin seed oil topically to the scalp to encourage hair growth. There is sound reasoning behind each approach and it’s even possible that both can be used together to have a synergistic affect. Pumpkin Seed Oil Supplements for Hair Growth One of the most common ways that people use pumpkin seed oil for hair growth is by adding it to their diet. Pumpkin seed oil is a nutrient-rich oil that is high in essential fatty acids, zinc, and vitamins A, C, and E — all of which are great vitamins for hair health. Pumpkin seed oil can be used to cook in the same way you might use other vegetable oils – although it does have a low smoke point, which doesn’t make it a great option for frying foods. If you don’t want to cook with pumpkin seed oil, it can also be taken as a supplement. You can find various pumpkin seed oil supplement products online in either gel capsule or tincture formats. Just make sure you find a product that is intended for eating, because there are also some topical treatment pumpkin seed oil products that may have added inedible ingredients. Pumpkin Seed Oil Effects on Hair Thickness A study published in the journal Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, tested whether adding pumpkin seed oil to one’s diet could be an effective treatment for male pattern baldness. In this double-blind, placebo controlled trial, 76 men suffering from male pattern baldness were given a daily supplement of either 400mg of pumpkin seed oil or a placebo pill. After 24-weeks the two groups of men were examined to see if there had been any substantial scalp hair growth. Incredibly, the men eating pumpkin seed oil for hair growth saw an average 40% increase in hair count! The patients receiving the daily pumpkin seed oil also reported significant improvements in their own perception of their hair growth and hair thickness. Although the patient sample size in this study was not very large, it still provides a very promising suggestion that daily pumpkin seed oil consumption could benefit men suffering from male pattern hair loss. Topical Pumpkin Seed Oil for Female Pattern Hair Loss A 2021 study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology tested how topical pumpkin seed oil treatments could compare to topical minoxidil treatments for women. Topical minoxidil is a commonly used over-the-counter pharmaceutical indicated to treat androgenetic alopecia conditions, including female pattern hair loss. However, topical minoxidil does have some potential negative side effects – which make topical pumpkin seed oil an appealing alternative (if it can work of course). In this study, 60 women with androgenetic alopecia were divided into two groups to receive daily applications of either topical minoxidil or topical pumpkin seed oil. After 3 months both groups were observed to determine the study outcomes. The researchers examined hair follicle health, hair thickness, and hair loss. They concluded that both groups showed statistically significant improvement! The researchers suggest that applying pumpkin seed oil on hair over time can stimulate hair growth in a significant amount of women suffering from hair loss. While the group that used pumpkin seed oil for hair growth saw impressive improvements, the researchers do note that more hair growth was observed in the topical minoxidil group. The researchers also acknowledge that more research is needed to gain a better understand of the effects of pumpkin seed oil on hair follicles. Effects of Pumpkin Seed Oil on DHT One of the main causes of androgenic alopecia is a hormone called dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. DHT binds to hair follicles and cause them to shrink over time, leading to thinning hair and eventually balding. Interesting, DHT is also involved in symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia – a prostate condition in men that may be linked to male pattern baldness. Some research has suggested that pumpkin seed oil may inhibit the production and activity of 5-alpha reductase — an enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT. A 2022 study tested how effective pumpkin seed oil is at inhibiting 5-alpha reductase enzymes on hair follicles. The study was quite successful, and researchers saw the pumpkin seed oil help prevent hair loss and even encourage healthy hair growth in a significant amount of test subjects. The researchers believe the hair growth observed was directly related to the DHT-inhibiting properties of the oil they derived from pumpkin seeds. It’s worth noting that there are a
Hair Loss Diet: Foods for Hair Growth and Thickness

Hair Loss Diet: Foods for Hair Growth and Thickness When it comes to treating hair loss, what you eat is just as important as the products you use. A good diet can help supply the essential nutrients your hair needs to stay strong and healthy. Eating a balanced diet of protein, complex carbohydrates, iron, Healthy fats and vitamins can contribute to healthier and thicker looking hair. When our diets are not meeting the nutritional needs of our bodies, our hair health can be one of the first things to be affected. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to hair loss. This means that in order to treat hair loss effectively and stimulate new hair growth, it is often essential to ensure that our diet is adequate. In this guide, we will overview the ways in which nutritional deficiency can lead to hair loss and discuss strategies to ensure that your diet includes everything your hair needs to grow thick and strong. Nutritional Deficiency and Hair Loss Nutritional deficiency can lead to a lot of problems with our body – including hair loss. When we do not get adequate amounts of essential vitamins and minerals, our bodies cannot carry out normal activities, including the production of new cells, including those used for hair growth. Nutritional deficiencies can be caused by a number of factors such as poor absorption due to digestive issues or inadequate intake from food sources. How Diet Affects Hair Follicles Your hair follicles require a number of essential vitamins, minerals and nutrients in order to remain healthy and produce new hair. A diet that is lacking in these components can lead to a decrease in the production of new hair cells, leading to hair loss. The hair growth cycle has three phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). The anagen phase, during which the hair follicles grow longer, can last two to six years. After the hairs fall out, they enter the catagen stage, a transitional phase that only lasts for two or three weeks. The final stage in this cycle is telogen phase, or the “resting phase”; at this point, the hair remains very tiny before re-entering into the growing phase again. The telogen phase, or “resting stage,” usually lasts 2-3 months. However, when our bodies are lacking certain nutrients, the resting phase can be extended. This means that new hairs are not being produced as quickly and your hair may start to thin out. Diet and Androgenetic Alopecia Androgenetic alopecia (also known as androgenic alopecia) is the most common type of hair loss, affecting both men and women. It occurs when testosterone and other male hormones interact with hair follicle cells to cause a decrease in the production of hair. Specifically, testosterone is converted to Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which disrupts hair growth. This type of alopecia is commonly known as male pattern hair loss or female pattern hair loss. While androgenetic alopecia has the same root causes in men and women, there are some differences in how it presents. People with male pattern hair loss will typically experience a receding hairline and/ or hair loss that starts from a spot on the back of the scalp. Meanwhile, female pattern hair loss is more likely to cause diffuse hair loss, with widespread thinning often most prominent along the part and hair line. Although there is no cure for this hair loss condition, there are certain dietary changes that can help slow down its progression. Vitamins such as Vitamin A, B complex, C and E are all essential for hair growth as they support cell reproduction and health. Minerals such as zinc, iron and magnesium are also important for maintaining strong and healthy hair follicles and preventing brittle hair. Protein is also an essential component of your diet – it helps build the keratin found in your scalp which makes up the bulk of your hairs structure. Foods to Promote Hair Growth In order to ensure that your diet is adequate for hair growth, it’s important to include plenty of foods high in certain nutrients that are linked to healthier hair. Here are some examples of foods that may help promote hair health and prevent further hair loss: Dark Leafy Greens Dark leafy greens like spinach, kale and Swiss chard are all packed full of vitamins A and C which help to promote healthy cell growth. These green leafy vegetables are also full of iron and calcium which has been shown to help maintain strong and healthy hair. Nuts & Seeds Foods like almonds, chia seeds and walnuts are great sources of protein, zinc and Vitamin E – which are all essential to promote hair growth and keep hair healthy. Legumes Lentils and beans are some of the highest iron and protein-rich plant foods available. Including these in your diet is a great way to protect hair follicles and prevent hair loss. Sweet Potatoes Sweet potatoes are a great source of Vitamin A – which is widely recognized as one of the most essential vitamins for growing healthier hair. Avocado Avocados contain biotin, a B-vitamin which has been shown to support hair growth and prevent hair loss. Eggs Eggs are also a great source of biotin, and a great vegetarian source of protein – both of which are crucial for preventing hair loss and promoting healthy hair. Fatty Fish Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, are packed full of omega-3 fatty acids that help to nourish and protect the scalp. Omega-3 also helps to reduce inflammation in the body which can help keep hair healthy. Red Meat Red meat is a great source of protein, iron and zinc – all of which are essential for hair growth. Although there are plenty of vegetable sources for these nutrients, it’s important to ensure that people on vegan or vegetarian eat plant foods with high nutritional value to avoid deficiencies in protein and iron which are linked to hair loss. Berries Berries are a great source
Dutasteride For Hair Loss: Dosage and Side Effects

Dutasteride For Hair Loss: Dosage and Side Effects Dutasteride is an FDA-approved medication that is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern hair loss. While Dutasteride is only FDA-approved to treat BPH, it is commonly perscribed “off label” for treating men with hair loss. Dutasteride works by blocking the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which in turn reduces the amount of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in your scalp. DHT is a hormone that shrinks hair follicles, leading to thinning hair and eventually baldness. By reducing DHT levels, dutasteride can help slow or even stop further hair loss and may even promote new growth. In this article we will discuss the commonly used dosages and potential side effects of dutasteride for hair loss. Dutasteride for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Although Dutasteride is commonly prescribed to treat male pattern baldness, this is technically considered an “off-label” use of this medication. Dutasteride is actually FDA approved for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition which causes an enlarged prostate. Men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia can experience issues related to prostate enlargement, including problems with urinary flow, erection decrease, decreased libido, and other side effects. Clinical studies have shown that Dutasteride can treat BPH. A 2013 study published in the journal Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy suggested that Dutasteride is an effective treatment for prostate enlargement and can improve symptoms as it significantly reduces prostate volume in some patients. Treating Hair Loss with Dutasteride Dutasteride is commonly prescribed as a medication used to treat male pattern hair loss. Studies have shown that patients with androgenetic alopecia are more likely to stop hair loss and start regrowing hair when they begin taking dutasteride. While there are other medications, such as finasteride and minoxidil, that are specifically FDA-approved for treating hair loss – there is some reason to believe that dutasteride could be just as effective for treating hair loss. Dutasteride Mechanism of Action Dutasteride works by inhibiting the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone into the androgen hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a hormone that shrinks hair follicles, leading to thinning hair and ultimately baldness. By reducing DHT levels, dutasteride can help slow or even stop further hair loss and may even promote new hair growth. The way that Dutasteride blocks DHT production is similar to how Finasteride combats hair loss. Both finasteride and dutasteride can be used to decrease the presence of androgenic sex hormones, including DHT, as a way of protecting hair follicles. These DHT blocking medications can be a particularly useful tool for regrowing hair, especially in individuals who have scalp hair that is sensitive to androgens. Can Dutasteride Treat Male Pattern Baldness? Male pattern baldness is a type of baldness that mostly affects men. It is caused by hormones that make the hair follicles shrink. This makes the hair thin and eventually fall out. Studies show that a combination of medications, including dutasteride, can be effective in treating this type of hair loss. In a randomized, placebo controlled, phase III study, oral Dutasteride was used to treat a group of men with male pattern baldness. In the study, some men were given a daily placebo pill and some were given daily 0.5mg pills of Dutasteride (brand name “Avodart”). The patients that took oral dutasteride, showed significantly less hair thinning than the group taking placebo – suggesting that dutasteride can be effectively used for the treatment of hair loss. Dutasteride and Androgenetic Alopecia Androgenetic Alopecia (also known as androgenic alopecia) is disease that causes hair thinning and hair loss in people who have scalp hairs with a sensitivity to the androgen hormone DHT. When there are high levels of DHT present on the scalp, it can make hair follicles shrink, which leads to thinning hair and eventually hair loss. The symptoms of androgenetic alopecia can vary depending on the person, but may include scalp hair thinning, a decrease in overall hair volume, bald patches, or a receding hairline. Fortunately, Dutasteride is a medication that helps with blocking DHT production, thus lowering DHT levels on the scalp. Like other hair loss medications, Dutasteride contains 5 alpha reductase inhibitors, which prevent the enzyme responsible for making DHT out of testosterone. Dutasteride vs Finasteride Doctors prescribe Finasteride and Dutasteride commonly for treating male pattern baldness. Both finasteride and dutasteride are 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. They work by blocking the enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT, which is a hormone responsible for thinning hair and baldness. The effectiveness of oral dutasteride compared to oral finasteride has been studied. A 2017 systematic review study concluded that in some studies oral dutasteride was shown to be more effective in treating androgenetic alopecia than oral finasteride. This study also concluded that the side effects of dutasteride were “comparable” to finasteride side effects. Although this is just one of many published studies, it suggests that when comparing dutasteride vs finasteride for treatment of hair loss in men, dutasteride may be the better option. Oral Minoxidil vs Oral Dutasteride Topical minoxidil and oral minoxidil are both prescribed by health care professionals for treating male pattern baldness. Oral minoxidl is less commonly used to treat hair loss in men and women than topical minoxidil because of the side effects associated with the oral version. Generally, patients prescribed topical minoxidil will see less common and less severe side effects than patients using oral minoxidil as a hair loss treatment. However, recent studies have shown that low doses of oral minoxidil can effectively treat hair loss in some patients in a relatively safe manner. If you are experiencing hair loss, it may be worth speaking with your healthcare provider to determine whether oral minoxidil or oral dutasteride would be a better option for stimulating hair growth. Each medication has it’s pros and cons, including potential adverse reactions. Oral dutasteride can’t be used by a pregnant woman and can lead to sexual dysfunction (including erectile dysfunction) in
Blocking DHT and Stopping Hair Loss

Blocking DHT and Stopping Hair Loss DHT, or dihydrotestosterone, is a hormone that can cause male and female pattern baldness when its levels become too high in the body and on the scalp. DHT causes hair loss when DHT binds itself to the hair follicles, causing them to shrink. The impact of excess DHT on hair follicles can lead to thinning of the hair and eventually balding. Fortunately, there are many different strategies for blocking DHT induced hair loss, including natural remedies, pharmaceuticals, and lifestyle changes. In this guide, we will discuss the root causes of DHT hair loss and the best, clinically supported, strategies for blocking DHT hair loss. What is DHT? DHT is a derivative of the sex hormone testosterone, and it’s important to understand the relationship between the two hormones. Testosterone is an anabolic hormone responsible for many bodily functions, including sexual development and libido. DHT is a byproduct of testosterone and has been linked to balding when its levels become too high in comparison to other hormones such as estrogen. Androgenetic Alopecia and DHT Androgenetic alopecia, also known as female or male pattern baldness, is the most common form of hair loss in both sexes. It affects up to 70% of men and 40% of women during their lifetime. Androgenetic alopecia is caused by the interaction between DHT and receptors in the scalp, leading to miniaturization of the hair follicles and eventual hair loss. Specifically, people with this type of alopecia may have DHT sensitivity, which can make them more likely to experience hair loss when their scalp hair is exposed to large amounts of this androgen hormone. DHT and Male Pattern Baldness Though there are many potential causes of hair loss, male pattern baldness is most frequently linked to a mix of genetic and hormonal elements. In particular, it’s commonly believed that this kind of hair loss can be inherited from one’s parents. Additionally, male sex hormones called androgens are thought to contribute to the development of androgenetic alopecia. Specifically, DHT is an androgen that has been found to be directly associated with male pattern baldness. Male pattern baldness typically starts with a receding hairline, followed by thinning of the hair at the crown. In some cases, this can eventually lead to complete baldness. The speed of progression and amount of hair loss associated with male pattern baldness will differ from person to person. DHT and Female Pattern Hair Loss Though it’s less common than male pattern baldness, female pattern hair loss is also caused by DHT. Women typically experience a diffuse thinning of the hair on their scalp rather than the receding hairline that men often have. In some cases, female pattern hair loss can cause bald spots or a completely bald scalp. In fact, there are at least 15 different types of alopecia and more than a few of them are linked to androgenic factors including DHT. How DHT Affects Hair Follicles In order to understand how DHT affects hair follicles, it’s important to understand the different stages of the hair growth cycle. The anagen phase is the active growth stage where new hairs are formed and existing ones get longer. During this stage, cells in the follicle divide rapidly while nourishing the newly formed strand with essential nutrients. The catagen phase is a transition period that follows during which the cells stop dividing and shrink back up into a club shape. This prepares them for the telogen phase, or resting phase, when no new hairs are made and older hairs eventually fall out. Eventually, a new anagen phase begins and the whole process starts over again. When DHT levels become too high on the scalp, the hair follicles can shrink and stop producing healthy strands of hair. This is known as miniaturization, and it’s one of the main effects of DHT on hair follicles. Eventually, this process leads to thinning and then complete loss of the affected hairs. In other words, DHT plays a key role in causing male pattern baldness and female hair loss. It’s also important to note that DHT levels don’t need to be abnormally high for this effect to occur – even regular or normal levels can cause issues if your scalp is sensitive enough to it. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can use to block DHT-induced hair loss and prevent further damage to your locks. How to Block DHT for Hair Growth The good news is that there are a number of hair loss treatments designed to reduce or even reverse the effects of DHT on your hair. For example, one strategy is to use DHT blocking medications such as finasteride (Propecia) or dutasteride (Avodart). These drugs work by blocking the 5-alpha reductase enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT. Alternatively, you can also try other hair loss treatments, including topical minoxidil, which helps stimulate hair growth and lengthen the anagen phase for thicker locks. Additionally, certain lifestyle choices can help to keep DHT levels under control. For instance, maintaining a healthy diet full of vitamins and minerals like zinc and iron can combat hair loss by promoting strong hair follicles and reduce shedding. Additionally, exercise is important for overall health and can help reduce stress levels, which can promote healthier hair growth. Finally, it’s important to note that some natural ingredients are known to have anti-DHT properties. For example, research suggests that saw palmetto might be able to block the 5-alpha reductase enzyme, while green tea and nettle root extract may also work as DHT blockers. DHT Blocking Medications In some cases, your doctor may recommend DHT blocker medications to block help stop hair loss. There are a few DHT blocking hair loss medications that are available in the US over-the-counter or by prescription: Finasteride Finasteride is a common prescription hair loss medication that targets androgens such as DHT in order to prevent or slow down miniaturization. It works by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into
Microneedling for Hair Loss
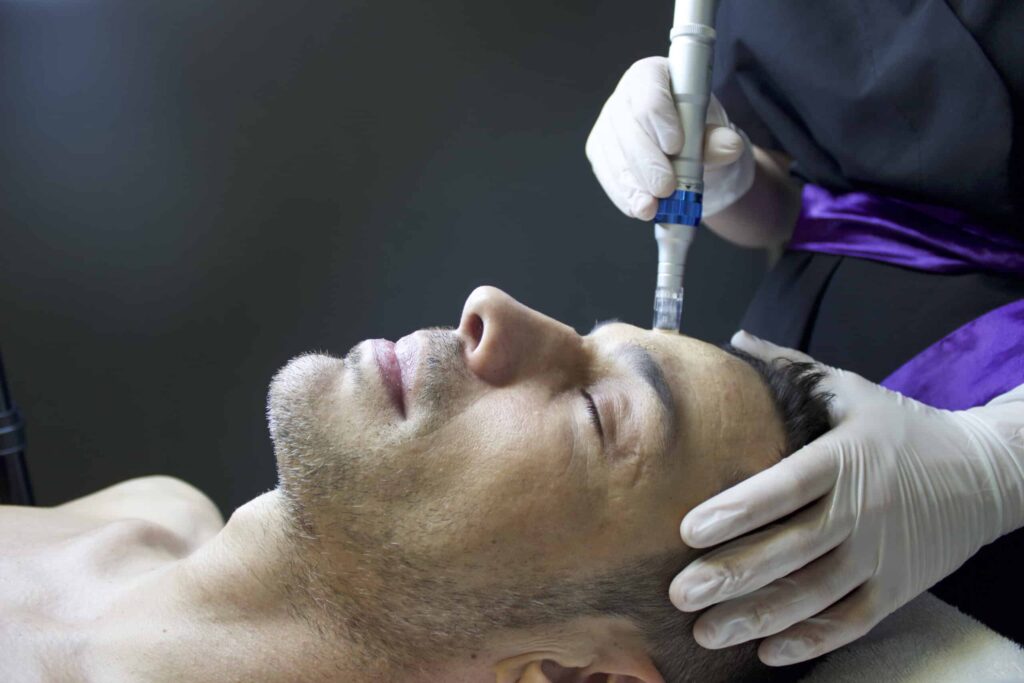
Microneedling for Hair Loss Microneedling is a cosmetic treatment that uses very tiny needles to puncture the skin and stimulate collagen production. It’s sometimes called dermarolling, micropuncturing, or percutaneous collagen induction therapy (PCIT). Microneedling has long been used to improve the appearance of wrinkles, scars, and stretch marks. More recently, microneedling is being used as a treatment for hair loss. In this article, we review the theory behind microneedling for hair loss, including the science supporting it and the available microneedling devices on the market. How Does Microneedling Promote Hair Growth? Microneedling for hair loss is based on the theory of wound healing. When the skin is wounded, it goes through a complex repair process that involves three main phases: Inflammation: In this phase, blood vessels dilate and inflammatory cells are recruited to the site of injury. This increased blood flow helps to clean up the area and prepare it for healing. Proliferation: In this phase, new cells are generated to replace the damaged tissue. Remodeling: In this phase, the new tissue is matured and remodeled to match the surrounding tissue. The needles in the microneedling device create tiny injuries in the skin, which triggers inflammation. This leads to the recruitment of new cells and the growth of new blood vessels. The new cells help to repair the damaged tissue and this can stimulate hair growth in some people. Microneedling for Androgenetic Alopecia Androgenetic alopecia (sometimes called androgenic alopecia) is the most common type of hair loss, affecting both men and women. It’s also known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern hair loss. Androgenetic alopecia is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. The main hormone involved is dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a byproduct of testosterone that has been shown to shrink hair follicles and inhibit hair growth. Common prescription medications to treat hair loss, including topical minoxidil and finasteride, can help reduce hair thinning associated with androgenic alopecia by directly reducing DHT production. Microneedling on the other hand, may not have a direct impact on DHT production, yet still has been shown to stimulate new hair growth in multiple clinical studies. Microneedling Effects on Hair Follicles The needles in a microneedling device create tiny injuries to the skin, which can stimulate the growth of new hair follicles. This is thought to occur through a couple of mechanisms: Stimulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is important for hair follicle development and regeneration. In one study, microneedling increased the expression of genes involved in this pathway, which led to the growth of new hair follicles. Release of Growth Factors Microneedling can also lead to the release of growth factors from the skin, which can promote the growth of new hair follicles. Growth factors are proteins that play an important role in cell growth and regeneration. One study found that microneedling increased the levels of epidermal growth factors and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) which are directly associated with hair regeneration. Dermal Papilla Stem Cells When the small needles of a microneedling device puncture scalp skin, they cause a healing cascade that stimulates the production of Hair Follicle Stem Cells in the “hair bulge” area underneath the hair follicle. This is believed to be one of the reasons why microneedling for hair growth can be effective. Microneedling vs. Topical Minoxidil Microneedling and minoxidil are two popular treatments for hair loss. Both have been shown to be effective in stimulating new hair growth, but there are some key differences between the two. Minoxidil is a topical medication that is applied to the scalp twice daily. It can take several months to see results from minoxidil lotion. In contrast, microneedling is a quick and easy procedure that can be done in-office by a trained professional. A review study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology in 2022 compared the effectiveness of microneedling and topical minoxidil in patients with androgenic alopecia. The study found that in general, there were more hair count increases in the microneedling group compared to the minoxidil group. The researchers further observe that the patients who received microneedling for hair loss, while also receiving topical minoxidil showed the best hair regrowth outcomes. This suggests that topical medications like minoxidil can be combined with a microneedling session to deliver overall more effective hair loss treatments. Platelet Rich Plasma vs. Microneedling Platelet rich plasma (PRP) is another popular treatment for hair health. Platelet rich plasma is made from a patient’s own blood and contains high levels of cells and proteins associated with hair regrowth. Microneedling therapy and PRP therapy have both been clinically shown to be effective treatments for male and female pattern hair loss. Microneedling treatment for hair loss is often done as a standalone procedure – however, many clinicians perform microneedling and delivery PRP injections simultaneously when treating hair loss disorders. One small study compared the efficacy of microneedling as a hair loss treatment with and without the addition of platelet rich plasma. This study found that patients who received PRP and microneedling for hair loss showed more hair regrowth than the patients who just received a microneedling treatment. If you want to learn more about PRP for hair loss – check out this guide. Microneedling for Alopecia Areata Alopecia areata (AA) is an autoimmune disorder that results in patchy hair loss. Unlike some other forms of alopecia, the exact mechanism of action between AA and hair loss is not fully understood. The hair loss associated with this condition is believed to be related to a variety of factors, including the immune system, stress, and genetics. While there is limited research on microneedling for alopecia areata, there are some promising case studies. This 2014 study showed success in treating two patients with alopecia areata who were not responding to more traditional therapies. After multiple scalp microneedling procedures were performed, both patients were able to regrow hair in their previously patchy bald spots.
Side Effects of Finasteride for Hair Loss

Side Effects of Finasteride for Hair Loss Finasteride is an FDA-approved medication that was originally created to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia. Today, Finasteride is primarily used to treat male pattern hair loss. Finasteride is most commonly prescribed as an oral medication under the brand name Propecia, although it can also be used as a topical medication. In both cases, Finasteride is a type of hormone therapy and works by inhibiting the conversion of Testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). When testosterone is converted into DHT, it can cause the hair follicles to shrink, leading to thinning hair and eventually baldness. While Propecia and other finasteride-based prescription medications can be an effective hair loss treatment, they also have a long list of harmful side effects. Some of the more serious side effects include sexual dysfunction, allergic reaction. Some studies even indicate that there may be a link between oral finasteride and and cancer in men. How Does Finasteride Treat Hair Loss? Finasteride is a type of 5-alpha reductase inhibitor. 5-alpha reductase is an enzyme that helps to convert testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a hormone that is responsible for many developmental changes in the body during puberty, including the enlargement of the prostate gland. In men, DHT is also responsible for causing male pattern hair loss. By inhibiting the production of 5-alpha reductase, Finasteride decreases the amount of DHT in the body, which can help to prevent hair loss and promote hair growth. Oral Finasteride (Propecia) There are two ways in which Finasteride can be used to treat hair loss. It can either be taken orally in pill form, or it can be used topically. When taken orally, Finasteride is typically prescribed as Propecia. Propecia is a brand name for the oral medication that contains 1mg of Finasteride. For the treatment of thinning hair, men are typically prescribed to take one 1mg tablet of Propecia per day. It may take several months before results are seen, and the full effects of Finasteride may not be realized for up to a year. Topical Finasteride When used topically, Finasteride is sometimes combined with other medications, such as minoxidil. Minoxidil is a medication that is applied directly to the scalp in order to promote hair growth. It is available over-the-counter in a variety of products, such as Rogaine. Finasteride is typically used in a 2% concentration when combined with minoxidil. It is important to note that topical finasteride is not FDA-approved for the treatment of hair loss and should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Additionally, unlike topical Minoxidil, topical Finasteride can not be purchased over-the-counter, and acquiring it will require first obtaining a prescription from a licensed health care professional. Finasteride for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Finasteride was originally FDA-approved in 1992 for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also known as enlarged prostate. BPH is a condition that affects many men as they age, and can cause urinary symptoms such as difficulty urinating and a need to urinate more frequently. Finasteride works to treat BPH by inhibiting the production of 5-alpha reductase, which decreases the amount of DHT in the body. By decreasing the amount of DHT, Finasteride can help to shrink the enlarged prostate gland – which can help improve urine flow. Finasteride is typically prescribed in 5 mg tablets to treat BPH. These 5 mg tablets, often under the brand name Proscar, are much larger than the 1mg tablets of Propecia used by most men for thinning hair. It’s important that men do not attempt to use these larger 5 mg finasteride tablets for thinning hair without permission from their doctor or pharmacist. The common side effects associated with this medicine have pose an increased risk with the larger 5 mg dosage. Propecia for Male Pattern Hair Loss The most common use for Finasteride is the treatment of male pattern baldness. Male pattern hair loss is a type of alopecia that occurs in men who are genetically predisposed to be sensitive to the effects of DHT. When exposed to DHT, these men may experience thinning hair, receding hairlines, and eventually complete baldness. Propecia is typically prescribed as a treatment for thinning hair in men because it can help to reduce the levels of DHT in the scalp, which can stop the progression of hair thinning and even promote new hair growth. Finasteride for Female Pattern Hair Loss While Finasteride is FDA approved to treat androgenetic alopecia in men, it is currently not approved for women. There are some concerns that finasteride use in women can cause adverse events. There is particular concern that finasteride could cause birth defects if the medicine is given to pregnant women. However, there are some recent studies indicating that oral finasteride may be well tolerated by women with androgenetic alopecia. Although further studies are needed, women with female pattern hair loss may consider speaking with their doctor or pharmacist to see if this medication could be right for them. Finasteride and Prostate Cancer There has been some concern that Finasteride may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. However, studies have shown that there is no increased risk of developing prostate cancer in men taking Finasteride for BPH or thinning hair. In fact, a 2020 review study showed that men who took Finasteride have a lower risk of developing prostate cancer than men who did not take the medication. This recent research has lead some to consider the use of finasteride as a preventative for men who are at risk of developing prostate cancer. Common Side Effects of Finasteride Finasteride has a long list of potential side effects, some of which can be quite serious. While not a complete list, here are some of the most commonly reported side effects: Depression from Finasteride A review study published in 2021 demonstrated a link between finasteride and depression in men. This link was shown to be independent from patient medical history and appears to demonstrate a clear link between oral finasteride
Laser Hair Growth Treatments – Reviewed
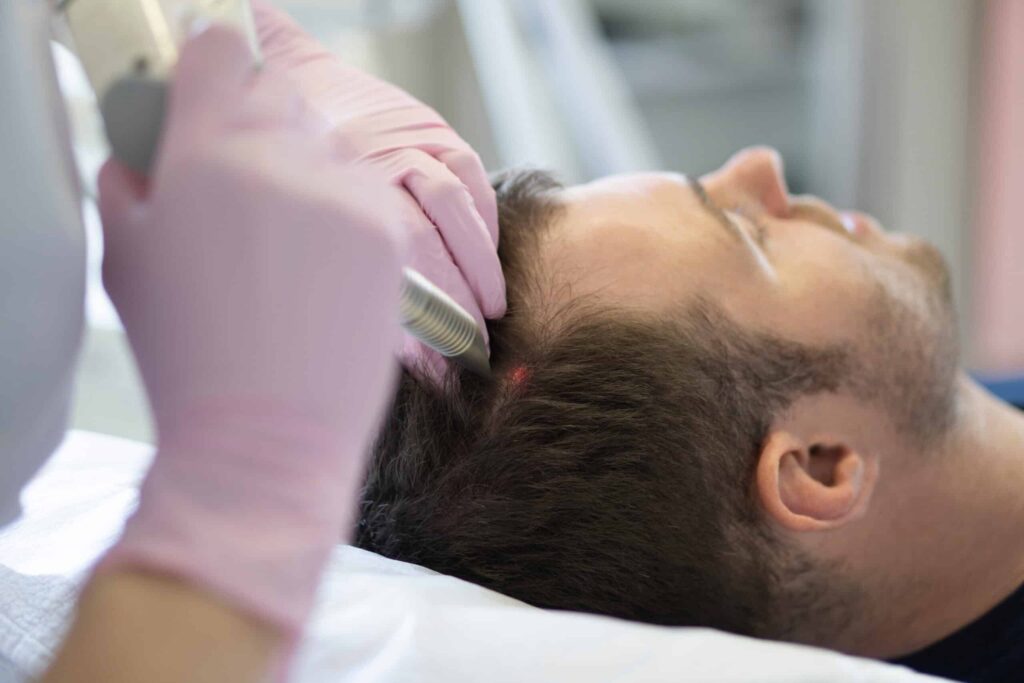
Laser Hair Growth Treatments – Reviewed If you’re considering laser hair growth treatments, it’s important to do your research and understand the potential risks and side effects. In this article, we’ll review the evidence for and against using lasers for hair growth, as well as the different types of laser treatments and products available. We will also discuss the mechanism of action behind laser hair growth and the science that supports it. Laser Hair Growth Treatment Options Lasers have been used for decades to treat various medical conditions, including hair loss. Laser therapy uses concentrated light to stimulate hair roots and promote hair growth. Light therapy for hair works through a process known as photobiomodulation and has been shown to be clinically effective in a number of published studies. Low Level Laser Therapy Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) is commonly used for the treatment of female pattern hair loss and male pattern hair loss. Several studies have shown that LLLT can increase hair density and thickness (including total hair count), as well as promote hair regrowth. However, not all studies have shown positive results, and the long-term effects of LLLT hair loss treatments are relatively unknown. LED Light Therapy LED (light emitting diode) light is also used to improve hair growth. The difference between an LED and laser treatment has mostly to do with the way light is directed. Lasers produce a coherent beam of light – which means all of the photons of light are traveling in the same direction. Whereas LED light spreads in many direction – similar to a common lightbulb. The good news is that LED lights and laser light have both been shown effective for hair regrowth. Laser hair growth products have been traditionally more popular than LED products. However, since LED lights are generally more affordable than laser diodes, there is a recent increase in LED products being sold to help regrow hair. Many of the popular “laser cap” devices available actually use LED’s instead of lasers. Red Light for Hair Follicles Red light therapy is a type of low-level laser therapy that uses red and near-infrared light to stimulate hair growth. Traditionally red light has been the popular choice for low level laser treatment devices. However, some recent research has shown that blue light may also be an effective way to stimulate hair growth. How Does Laser Therapy Promote Hair Growth? It’s thought that laser therapy can stimulate hair and promote hair growth by increasing blood flow and oxygen to the scalp, as well as by increasing the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a molecule that plays an important role in cell metabolism. This process of increased blood flow and ATP production is called photobiomodulation therapy (also known as PBM therapy or PBMT). Are There Any Side Effects Associated with Laser Therapy? Laser therapy is generally safe when performed by a trained professional. The most common side effects are temporary redness, itching, and swelling of the skin. In rare cases, more serious side effects, such as burns or eye damage, can occur. Is Laser Hair Growth Treatment Effective? The effectiveness of laser therapy for hair growth is still being investigated. Some studies have shown positive results, while others have not. The long-term effects of laser therapy are also unknown. If you’re considering laser therapy for hair growth, it’s important to consult with a board-certified dermatologist or other qualified healthcare provider to discuss the risks and benefits. Lasers for Hair Growth vs. Laser Hair Removal It’s important to note that there are two different types of lasers: those used for hair growth and those used for laser hair removal. Hair growth lasers use low-level light to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. Hair removing lasers, on the other hand, use high-level light to destroy body hair follicles in order to cause people to lose hair and prevent future hair growth. Laser Therapy for Female Pattern Hair Loss Female pattern hair loss, also known as androgenic alopecia, is the most common type of hair loss in women – affecting an estimated 50 million women worldwide. While there are a number of ways to treat androgenic alopecia, low level lasers are one of the more promising options. A 2014 study showed that low fluence red laser devices were effective in treating women with female pattern hair loss. This sham device controlled study demonstrated that laser hair growth devices were effective at stimulating new hair growth in women who had experienced hair loss. Laser Therapy for Male Pattern Baldness Male pattern baldness is the most common type of hair loss that affects most men at some point in their life. A review study published in 2021 concluded that laser hair growth products, including laser combs and laser cap devices are effective for treating men with male pattern baldness. According to this study, the available clinical evidence suggests that laser treatments, including those from laser cap devices, are an effective way to treat hair loss in men. Additionally, the study suggests that laser treatment can impact the hair growth cycle and actually increase hair thickness and lead to the growth of more hair in patients suffering from a receding hairline. Although not all patients in the studies reviewed saw significant improvements from laser cap devices, there was enough success to demonstrate that, overall, laser hair products outperform placebo devices for growing new hair. Laser Therapy for Androgenic Alopecia Androgenic alopecia (also known as androgenetic alopecia) is the medical term for hair loss caused by hormones. This type of hair loss can affect both men and women, but it’s more common in men. Laser hair growth products and other hair loss treatments, including minoxidil ( Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia), have all been shown effective for treating hair loss in clinical trials. Laser Light and Hair Follicle Stem Cells Light energy has been been clinically shown to have a direct impact on thinning hair by affecting the hair follicle. Although the exact mechanism of action
Hair Loss from Birth Control Pills

Hair Loss from Birth Control Pills Oral contraceptives are one of the most widely used forms of birth control. Birth control pills effectively prevent pregnancy by modulating the body’s production of hormones. Unfortunately, this method of hormonal birth control can have undesirable side effects, including hair loss. With nearly one in four women using hormonal contraceptives, it’s important to understand the link between birth control pills and hair loss. Can Birth Control Cause Hair Loss? With a lot of conflicting information online, it’s first important to understand the answer to this fundamental question: Can birth control cause hair loss? Unfortunately, according to a number of peer-reviewed studies, the answer is yes. Studies have shown that hormonal birth control methods, including oral contraceptives, have a direct link to hair growth and can contribute to hair shedding and female pattern hair loss. Understanding Hormonal Contraception Birth control pills work by modulating hormones in the body to prevent unwanted pregnancy. All oral contraceptives contain progestin, a synthetic form of progesterone – a naturally occurring sex hormone. Progesterone plays an important role in regulating the menstrual cycle and the early stages of pregnancy. When levels of progesterone are too low, it can cause irregular menstrual bleeding. However, when levels of progesterone are too high, it can have the opposite effect – halting menstruation altogether. This is ultimately the desired affect of a hormonal contraceptive. Cause of Birth Control Hair Loss While high progesterone levels effectively prevent pregnancy, they can also impact other bodily functions and cause unwanted side effects. Some of the side effects from hormonal birth control include weight gain, acne, mood changes, decreased libido, and hair loss. The progestin in hormonal contraceptives have been clinically shown to bind to androgen receptors – which results in increased androgenic activity. Androgens are male “sex hormones” that are present in both men and women in small amounts. When levels of these male hormones (including testosterone levels) rise, they can increase the production of Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a testosterone metabolite that has been shown to cause hair loss by interfering with hair follicles. The increased production of androgen hormones, and consequently DHT, on the scalp is believed to be directly related to hair shedding in women. It’s believed that there is even a greater risk of hair thinning and hair shedding for women with a strong predisposition to androgen sensitivity, including women with PCOS. How DHT Affects Hair Follicles Our hair grows in a natural cycle when our bodies are healthy and producing normal hormone levels. During this normal process, each follicle produces a new strand of hair which will grow for years until it eventually falls out. The first phase is known as the anagen phase or “growth phase,” which is when the hair follicles are growing longer. This growth period can last anywhere from two to six years. After the hairs fall out, they enter what’s called the catagen stage – a transitional phase that only lasts for two or three weeks. The final stage in this hair growth cycle is referred to as telogen phase, or the “resting phase,” where the hair remains very tiny before re-entering into the growing phase again. The hair follicle resting stage usually lasts a few months. However, during times of increased DHT production due to hormonal contraception use, the hair follicle can enter an extended resting phase, causing a lack of hair regrowth and eventually leading to hair thinning and female pattern hair loss. The effects of DHT on hair thinning are likely more prevalent in women with a genetic hair loss predisposition – including a family history of hair thinning issues. Combination Vs. Progestin-Only Pills It’s important to note that not all birth control pills contain the same type or amount of progestin. There are two main types of contraceptive pills: Progestin-Only Pills Contraceptive pills known as “mini-pills” contain only synthetic progestin, and no estrogen. They are often used by women who cannot take estrogen for medical reasons. Combination Pills Combination pills contain both progestin and estrogen. Estrogen is thought to offset some of the negative side effects associated with progestin, including hair loss. Studies have shown that estrogen can counteract the androgenic effects associated with hair loss by increasing sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). SHBG binds to testosterone in the body and ultimately, is believed to reduce the production of hair damaging DHT. For this reason, combination birth control pills may be less likely to lead to hair loss than progestin mini-pills. Birth Control Pill Androgen Index When choosing a birth control pill, it’s important to consider the androgen index – which is a measure of how androgenic a given pill is. Androgenic refers to the degree to which a hormone or medication can cause masculinizing side effects like hair loss. The androgen index is represented on a scale from 1 to 100. High Androgen Index Birth Control Pills Norethindrone oral contraceptives, sold under the brand names Ortho Micronor and Aygestin are progestin-only birth control pills. Often called “mini-pills,” these first-generation birth control pills contain no estrogen have have the highest androgen score among any prescription contraceptive pills. Medium Androgen Index Birth Control Pills Levonorgestrel is a progestin used in some second-generation combination birth control pills that fall within the medium androgen index. Levonorgestrel is the progestin used in some hormone-releasing IUD’s, including the Mirena IUD. Levonorgestrel is also the active ingredient in the emergency oral contraceptive Plan B. Low Androgen Index Birth Control Pills These low androgenic third-generation birth control pills include those that use the progestin Desogestrel – which is sold under the brand names Mircette, Kariva, Desogen, and Ortho-Cept. Other low androgen birth control pills are those containing the active ingredient Norgestimate, which is sold under the brand names Ortho Tri-Cyclen and Previfem. Antiandrogenic Birth Control Pills There is a new class of Antiandrogenic birth control pills that recently gained FDA approval. Drospirenone is one of these new progestins and it is the active ingredient along with ethinyl
Stress-Induced Hair Loss: Symptoms and Treatments

Stress-Induced Hair Loss: Symptoms and Treatments People can experience hair loss for a variety of different reasons. Thinning hair can be attributed to genetics, diet, disease, and even stress. Since stress is such a common element in our lives, it’s no wonder that hair loss from stress is a growing concern. Stress Hormones and Hair Loss Stress can cause hair loss by causing the body to produce higher levels of the hormone cortisol. Cortisol is a “stress hormone” released from the adrenal glands in response to physical or emotional stress and has many different effects on the body. One of the undesirable affects of this stress hormone is a negative impact on hair health. In addition, when cortisol levels are high, it can lead to inflammation of the scalp, which can also contribute to hair loss. Ultimately, the stress related hair thinning can lead to temporary hair loss in the form of telogen effluvium or more permanent thinning in the form of alopecia areata. Stress Interrupts the Natural Hair Growth Cycle When our bodies are healthy and under normal levels of stress, our hair grows in a natural cycle. During this normal hair cycle, each follicle produces a new hair, which grows for years and then eventually falls out. The first phase is called the anagen phase. This is the growth phase, when the hair is growing longer – and it lasts for two to six years. After the hair falls out, it enters the second phase of growth called the catagen phase. This is a transitional stage and it only lasts for two to three weeks. The last stage in the hair growth cycle is called the telogen phase. This is the “resting phase,” when the hair rests as a tiny vellus hair before it re-enters the growing phase. Under normal, healthy conditions, the Telogen phase can last for up to four months. However, when the body is experiencing a stressful event the hair follicle can enter an extended resting phase, which prevents hair regrowth and leads to thinning scalp hair. Stress and Telogen Effluvium When stress causes hair loss, it is often diagnosed as a condition called telogen effluvium. This is a temporary form of hair loss that occurs when the body experiences a traumatic event, such as childbirth, surgery, a high fever, or severe illness. However, this hair loss doesn’t just occur from physical stress – it can also occur when people experience stress from profound negative emotions, such as a breakup of the loss of a loved one. When the body is under stress, it pushes more hairs into the telogen phase, which is commonly known as the “resting phase.” In this phase, the hair follicle does not grow new hair. Fortunately, telogen effluvium hair loss is usually only temporary and the hair will typically grow back once the stressful event has passed. However, in some cases, telogen effluvium can lead to chronic hair loss if the individual continues to experience high levels of stress. Impact of Stress on Hair Follicles The hair follicles on our scalp follow a hair growth cycle that consists of three phases: growth, rest, and shedding. The growth phase (anagen) is when the follicle produces new hair. The resting phase (telogen) is when the follicle remains inactive for a period of time. And the shedding phase (catagen) is when the follicle dies and the hair falls out. When we’re stressed, it can cause the hair follicle to go into the resting phase sooner than they should. This can lead to thinning hair and eventually hair loss. Stress can also cause the follicles to produce weaker hairs that are more likely to fall out. Alopecia Areata One of the more serious stress-related hair loss conditions is called alopecia areata. This is an autoimmune disorder that can cause patchy hair loss all over the scalp or even complete baldness. Alopecia areata is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including stress. While there is no cure for alopecia areata, there are some treatments that can help regrow hair or camouflage the hair loss. These include corticosteroid injections, topical immunotherapy, and light therapy. Impact of Stress on Hair Follicle Stem Cells Each hair follicle on our scalp depends on special stem cells called hair follicle stem cells (HFSC) to promote hair growth. Recent research by the Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) has shown that stress can directly impact the sustained production of these important cells. The findings by Harvard researchers were supported by a 2021 study published in Nature that showed stress hormones caused the hair follicles on mice to enter a prolonged resting phase. The researchers at Harvard determined that chronic stress impacts how often hair follicle stem cells are able to regenerate. When the hair follicle stem cells fail to properly regenerate, the body lacks the critical tools needed to regenerate hair follicles which are responsible for promoting hair growth. Essentially, this study identifies the biological mechanism by which chronic stress leads to hair loss. Specifically, researchers found that chronic stress prevented dermal papilla cells from secreting Gas6, a molecule that is responsible for activating stem cells in the hair follicle. Non-Stress-Related Causes of Hair Loss While we’ve been discussing types of hair loss related to stress, it’s important to note that there are a number of non-stress-related causes of hair loss – including androgeneic alopecia, traction alopecia, and chemo induced alopecia. Androgenic alopecia Androgenic alopecia (also known as androgenetic alopecia) is the most common type of hair loss and is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. In this condition, the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) has been shown to be responsible for causing hair follicles to shrink and eventually stop producing hair. Traction Alopecia Traction alopecia is a type of hair loss that is caused by chronic hair pulling, typically from hairstyles that put stress on the hair follicles. Excessive hair pulling from tight hairstyles like braids or
