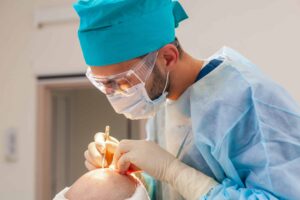
Do Hair Transplants Work? Types, Side Effects, and Photos
Do Hair Transplants Work? See Before and After Photos Hair transplant surgery is a procedure that has been performed for many years. It is designed to restore hair in bald or thinning areas of the scalp. There are different types